100% Free Ray Optics Mock Test for TGT PGT Physics 2025: 30+ Key MCQs [Bilingual]
At Physics Scholar by Anup Sir, we’re committed to helping you ace your exams with our 100% free practice mock test on Ray Optics, featuring 40+ most important MCQs in bilingual format (English and Hindi).

Are you preparing for TGT or PGT Physics examinations and looking for a reliable way to master Ray Optics? Look no further! At Physics Scholar by Anup Sir, we’re committed to helping you ace your exams with our 100% Free Ray Optics Mock Test, featuring 30+ most important MCQs in bilingual format (English and Hindi).
This article is your one-stop resource for revising key concepts, memorizing critical formulas, and testing your knowledge with a carefully curated quiz. Whether you’re a beginner or aiming to polish your skills, this free mock test will boost your confidence and exam readiness.
Ray Optics is a high-weightage topic in TGT and PGT Physics exams, often contributing significantly to your score. To help you excel, we’ve included a list of key points, a formula table, and a free practice test. Plus, we’ve added FAQs with one-liners and concepts frequently asked in exams to ensure you’re fully prepared. Let’s dive in!
Why Ray Optics is Crucial for TGT PGT Physics Examinations
Ray Optics (or Geometrical Optics) forms the foundation of optics in physics and is a must-master topic for TGT and PGT exams. Questions from this chapter test your understanding of concepts like reflection, refraction, lenses, mirrors, and optical instruments. With the right preparation, you can score full marks in this section!
To make your preparation seamless, we’ve also created free practice tests for other essential topics like Units & Dimensions, Vector Algebra, Straight Line Motion, and Circular Motion. Don’t forget to check out our ![]() 100% Free Fundamental Course for All PGT Physics Examinations with Handwritten Class Notes PDF for comprehensive study material.
100% Free Fundamental Course for All PGT Physics Examinations with Handwritten Class Notes PDF for comprehensive study material.
Watch This Playlist Lectures before attempting the below Free Ray Optics Mock Test
Key Points to Remember in Ray Optics for TGT PGT Physics Exams
Before jumping into the Free Ray Optics Mock Test, let’s quickly revise the most important concepts in Ray Optics that are frequently tested in TGT and PGT Physics exams. These points are designed to help you recall critical ideas and tackle direct questions:
- Laws of Reflection: The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, and the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie in the same plane.
- Laws of Refraction (Snell’s Law): The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant, given by
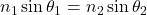 .
. - Total Internal Reflection: Occurs when the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle, leading to complete reflection within the denser medium.
- Mirror Formula: For spherical mirrors,
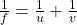 , where
, where 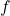 is focal length,
is focal length, 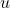 is object distance, and
is object distance, and  is image distance.
is image distance. - Lens Formula: Similar to mirrors,
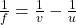 for thin lenses.
for thin lenses. - Magnification: For mirrors and lenses, magnification
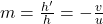 , where
, where 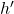 is image height and
is image height and 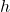 is object height.
is object height. - Refraction at Spherical Surfaces: Uses the formula
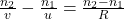 .
. - Optical Instruments: Understand the working of microscopes, telescopes, and their magnifying powers.
- Dispersion and Deviation: Study the splitting of light into colors and the deviation caused by prisms.
- Sign Convention: Follow the Cartesian sign convention for mirrors and lenses to avoid calculation errors.
These points are your quick revision guide. Keep them handy while solving MCQs or reviewing Physics Scholar by Anup Sir’s handwritten notes from our free fundamental course.
Essential Ray Optics Formulas for TGT PGT Exams
Formulas are the backbone of solving Ray Optics questions. Below is a concise formula table covering the most important equations you need to memorize for TGT and PGT Physics exams, formatted in table:
| Concept | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mirror Formula | Relates focal length, object, and image distances for mirrors | |
| Lens Formula | Relates focal length, object, and image distances for lenses | |
| Magnification (Mirrors/Lenses) | Calculates magnification for mirrors and lenses | |
| Snell’s Law | Governs refraction at the interface of two media | |
| Critical Angle | Condition for total internal reflection | |
| Lens Maker’s Formula | Calculates focal length of a lens | |
| Power of a Lens | Power of a lens in diopters | |
| Refraction at Spherical Surface | Relates object and image distances for spherical surfaces | |
| Prism Deviation | Deviation angle in a prism | |
| Magnifying Power (Microscope) | Magnification of a compound microscope | |
| Magnifying Power (Telescope) | Magnification of an astronomical telescope |
Pro Tip: Memorize these formulas and practice applying them in numerical problems. Pair this with our free practice tests on Units & Dimensions and Vector Algebra to strengthen your foundational knowledge.
Practice with Our Free Ray Optics Mock Test
Ready to test your Ray Optics knowledge? Our 100% Free Ray Optics Mock Test contains 40+ carefully selected MCQs covering all key concepts of Ray Optics. These questions are bilingual (English and Hindi) to cater to all TGT and PGT aspirants. The test is designed to mimic the actual exam pattern, helping you assess your preparation and identify areas for improvement.
After completing the test, review your answers and revisit the key points and formulas above. For more practice, explore our free tests on Straight Line Motion and Circular Motion to ensure a well-rounded preparation.
Why Choose Physics Scholar by Anup Sir?
At Physics Scholar by Anup Sir, we understand the challenges faced by TGT and PGT Physics aspirants. That’s why we provide free resources, including practice tests, handwritten notes, and fundamental courses, to make your preparation stress-free and effective.
Our 100% Free Fundamental Course for All PGT Physics Examinations with Handwritten Class Notes PDF is a must-have resource for every aspirant. It covers all major topics, including Ray Optics, in a concise and easy-to-understand format.
Our goal is to empower you with the tools and confidence to excel in your exams. Follow Physics Scholar by Anup Sir for more free content, tips, and updates tailored for Physics aspirants!
FAQs: Ray Optics for TGT PGT Physics Examinations
Here are some frequently asked questions about Ray Optics, including one-liners and key concepts commonly tested in TGT and PGT exams, with formulas in LaTeX:
Q1. What is the mirror formula, and how is it used?
A: The mirror formula is ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the focal length,
is the focal length, ![]() is the object distance, and
is the object distance, and ![]() is the image distance. It’s used to calculate the position of the image formed by spherical mirrors.
is the image distance. It’s used to calculate the position of the image formed by spherical mirrors.
Concept: Understand the sign convention and practice numericals to master its application.
Q2. What is total internal reflection?
A: Total internal reflection occurs when light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, and the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle, given by ![]() , causing complete reflection.
, causing complete reflection.
Concept: Critical for understanding optical fibers and prisms.
Q3. What is the lens maker’s formula?
A: The lens maker’s formula is ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the refractive index, and
is the refractive index, and ![]() ,
, ![]() are the radii of curvature of the lens surfaces.
are the radii of curvature of the lens surfaces.
Concept: Essential for calculating the focal length of lenses.
Q4. How is the power of a lens defined?
A: Power of a lens is ![]() (in meters), measured in diopters.
(in meters), measured in diopters.
Concept: Higher power indicates a shorter focal length, crucial for lens combination questions.
Q5. What is the magnifying power of a telescope?
A: The magnifying power of a telescope is ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the focal length of the objective lens, and
is the focal length of the objective lens, and ![]() is the focal length of the eyepiece.
is the focal length of the eyepiece.
Concept: Tested in questions about optical instruments.
Q6. Why does dispersion occur in a prism?
A: Dispersion occurs because different wavelengths of light refract at different angles due to the varying refractive index of the prism for each color.
Concept: Key to understanding rainbows and prism-based questions.
For more in-depth explanations, download our free handwritten notes from the Physics Scholar by Anup Sir fundamental course.
Conclusion
Mastering Ray Optics is a game-changer for TGT and PGT Physics aspirants. With our 100% Free Ray Optics Mock Test featuring 40+ bilingual MCQs, key points, and a formula table, you’re well-equipped to tackle this high-scoring topic.
At Physics Scholar by Anup Sir, we’re here to support your journey to success. Take the now, revise the concepts, and share this article with fellow aspirants. Let’s conquer Ray Optics together and ace your TGT/PGT Physics exams!


sir help me to prepare my exam from my home .they are doing great job ….