Top 100% Free Circular Motion Mock Test: Key TGT PGT & NEET Physics MCQs with Formulas & Notes
Master circular motion with our 100% free mock test for TGT, PGT, and NEET Physics! Get NCERT-based formulas, bilingual MCQs, concepts, and notes. Practice now!

Hey aspirants! Circular motion is a game-changer for TGT, PGT, and NEET Physics exams, and I’ve seen many students struggle with its concepts like centripetal force and banking of roads. As part of my 100% Free Physics Practice Test Series, I’m excited to share this mock test to help you master this NCERT Class 11 topic (Chapter: Motion in a Plane).
You’ll get a formula table, bilingual MCQs, and tips I’ve crafted from years of teaching. Plus, check out my other free tests to build your Physics skills:
Circular Motion Formulas (NCERT & NEET)
Let’s start with the must-know formulas for circular motion, straight from NCERT Class 11 and NEET syllabus. These are your toolkit for solving TGT, PGT, and NEET questions.
| Concept | Formula | Description | Alt Text |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centripetal Acceleration | Acceleration towards the center, | Centripetal acceleration formula | |
| Centripetal Force | Force towards center, | Centripetal force formula | |
| Angular Velocity | Rate of angular displacement, | Angular velocity formula | |
| Angular Acceleration | Rate of change of angular velocity, | Angular acceleration formula | |
| Linear-Angular Relation | Links linear and angular quantities. | Linear-angular relation formula | |
| Banking of Roads (No Friction) | Banking angle | Banking of roads formula | |
| Banking with Friction | Max speed with friction coefficient | Banking with friction formula | |
| Conical Pendulum | Time period, | Conical pendulum formula | |
| Vertical Circular Motion (Top) | Tension at top, min speed | Tension at top formula | |
| Vertical Circular Motion (Bottom) | Tension at bottom, min speed | Tension at bottom formula | |
| Motion in Magnetic Field | Radius for charge | Magnetic field path formula | |
| Non-Uniform Circular Motion | Total acceleration from centripetal ( | Non-uniform circular motion formula |
Source: NCERT Physics Class 11 (Chapter 4), NEET syllabus, TGT/PGT curricula.
Tip: Memorize these formulas and practice with our Vector Algebra Test to strengthen related skills!
Tutorial on Circular Motion by Anup Sir [Physics Scholar]
Struggling with banking or vertical circular motion? My YouTube tutorial breaks it down with solved examples and exam tips. Watch it below and subscribe for more!
Free Circular Motion Mock Test
Ready to test your skills? This mock test, part of our 100% Free Physics Practice Test Series, features bilingual (English/Hindi) MCQs for TGT, PGT, and NEET aspirants. Try it now and explore more:
Important MCQs with Explanations
Here are 5 must-do MCQs (English first, Hindi second, options in English/Hindi) to solidify your circular motion concepts. These are common in TGT, PGT, and NEET exams.
- What provides the centripetal force for a car on a flat road?
सपाट रास्ते पर कार के लिए अभिकेन्द्री बल क्या प्रदान करता है?
A) Frictional force / घर्षण बल
B) Gravitational force / गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल
C) Normal force / अभिलंब बल
D) Tension force / तनाव बल
Answer: A) Frictional force / घर्षण बल
Explanation: Friction between tires and road provides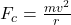 . Practice similar force questions in our Straight Line Motion Test. (TGT/PGT)
. Practice similar force questions in our Straight Line Motion Test. (TGT/PGT) - A 2 kg body moves in a 4 m radius circle at 8 m/s. What is the centripetal force?
2 किग्रा का पिंड 4 मीटर त्रिज्या के वृत्त में 8 मी/से से गति करता है। अभिकेन्द्री बल क्या है?
A) 32 N / 32 न्यूटन
B) 64 N / 64 न्यूटन
C) 16 N / 16 न्यूटन
D) 128 N / 128 न्यूटन
Answer: A) 32 N / 32 न्यूटन
Explanation: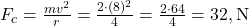 . (NEET)
. (NEET) - What is the time period of a conical pendulum of length 1 m at 45° with vertical? (
 )
)
1 मीटर लंबाई का शंक्वाकार लोलक ऊर्ध्वाधर से 45° कोण बनाता है। इसका समयावधि क्या है? ( )**
)**
A)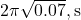 /
/ 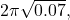
B)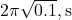 /
/ 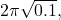
C)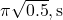 /
/ 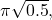
D)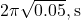 /
/ 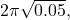
Answer: A)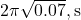 /
/ 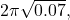
Explanation: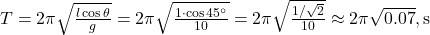 . (PGT)
. (PGT) - What is the minimum speed at the top of a vertical circle of radius 1 m? (
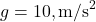 )
)
1 मीटर त्रिज्या के ऊर्ध्वाधर वृत्त के शीर्ष पर न्यूनतम चाल क्या है? (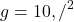 )**
)**
A)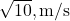 /
/ 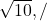
B)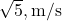 /
/ 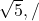
C)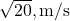 /
/ 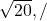
D)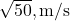 /
/ 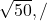
Answer: A)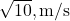 /
/ 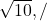
Explanation: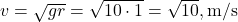 . Try related questions in our Projectile Motion Test. (NEET)
. Try related questions in our Projectile Motion Test. (NEET) - If a particle’s speed in circular motion is halved, how does the centripetal force change?
यदि वृत्तीय गति में कण की चाल आधी हो, तो अभिकेन्द्री बल में क्या बदलाव होता है?
A) Quadruples / चार गुना
B) Doubles / दोगुना
C) Halves / आधा
D) One-fourth / एक-चौथाई
Answer: D) One-fourth / एक-चौथाई
Explanation: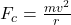 . If
. If  becomes
becomes 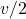 ,
, 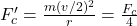 . (TGT/NEET)
. (TGT/NEET)
FAQs: One-Liner Conceptual Questions on Circular Motion
These quick answers tackle common doubts to help you and boost SEO.
- What is centripetal force?
A real force (e.g., tension, gravity) towards the center,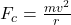 .
. - Is centrifugal force real?
No, it’s a pseudo force felt in non-inertial frames. - Why are roads banked?
To provide centripetal force via normal force, reducing friction. - What’s the minimum speed at the bottom of a vertical circle?
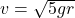 , ensuring loop completion.
, ensuring loop completion. - What happens if a string breaks in circular motion?
The object moves tangentially due to inertia. - How is angular acceleration related to tangential acceleration?
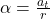 , where
, where 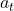 is tangential acceleration.
is tangential acceleration. - What’s the role of friction in banked roads?
Increases max speed: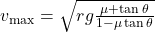 .
. - What is a conical pendulum?
A pendulum with a bob moving in a horizontal circle, period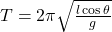 .
. - Why is tension minimum at the top of a vertical circle?
Gravity aids centripetal force: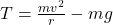 .
. - What’s the radius of a charged particle’s path in a magnetic field?
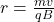 , based on mass, velocity, charge, and field.
, based on mass, velocity, charge, and field.
Conclusion
Aspirants, you’re one step closer to acing TGT, PGT, and NEET Physics with our 100% Free Physics Practice Test Series! This circular motion mock test, paired with my YouTube tutorial, will sharpen your skills. Keep practicing with our other free tests:
- Projectile Motion Practice Test
- Straight Line Motion Practice Test
- Vector Algebra Practice Test
Share this on X, WhatsApp, or Telegram to help fellow students, and let me know your feedback on my YouTube channel!


Very very helpful test to check the basics about chapter
Keep providing these types of test
Thank you, ma’am.
Questions thik the but thoda aur moderate kejiye
Thank you sir
Wow,Bahut Bahut sukriya Anup sir ànd team members of physics scholar aise test ke liye ,mja aa gya test dekar
[…] for other essential topics like Units & Dimensions, Vector Algebra, Straight Line Motion, and Circular Motion. Don’t forget to check out our 100% Free Fundamental Course for All PGT Physics Examinations with […]